Here at Geneious Biologics we are still working from home, but we may soon return to the office depending on what the New Zealand government recommends. We have been busy and have recently released a number of features and improvements to Geneious Biologics that you might like to try out.
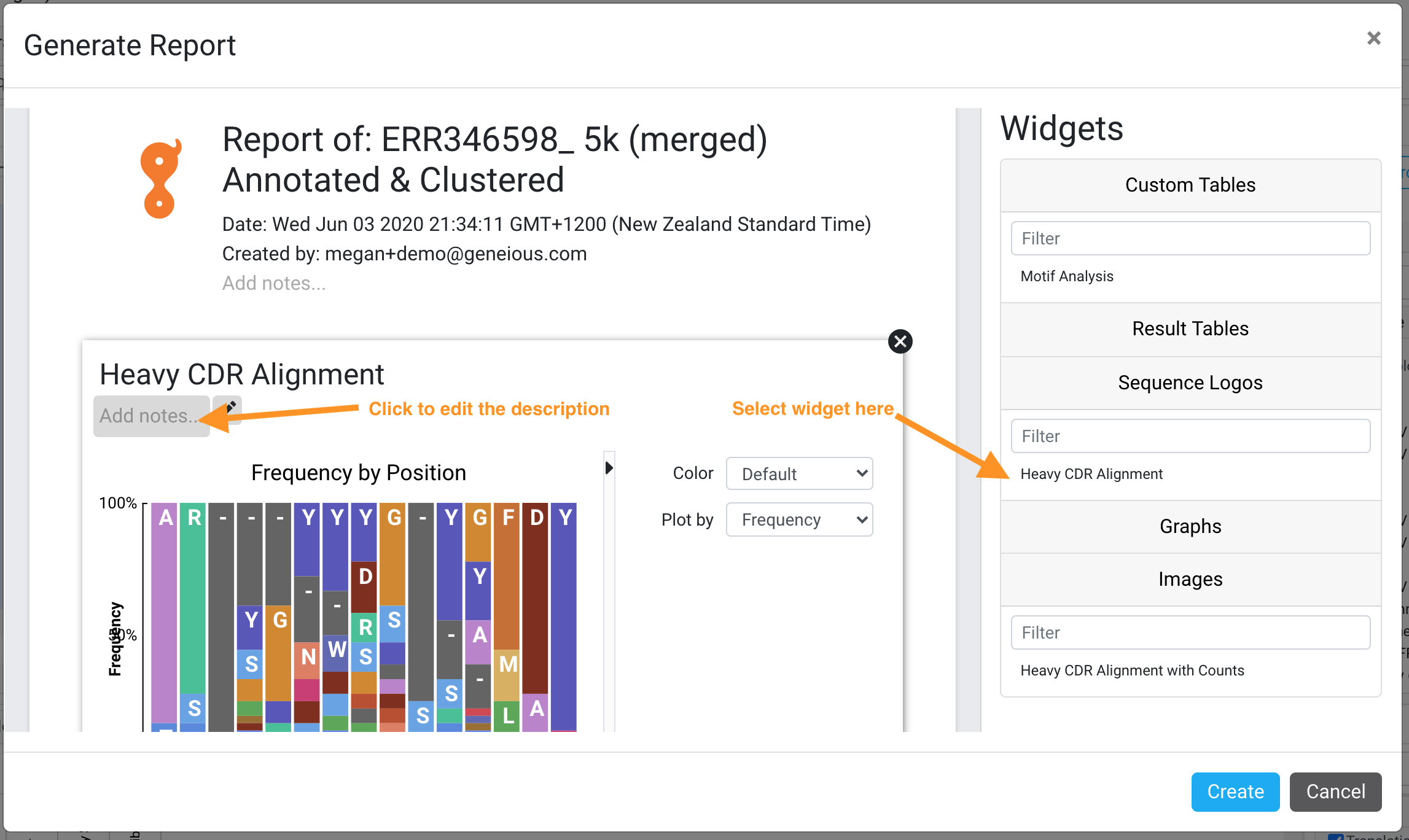
Dynamic Reporting
You can now create custom reports from your analysis results. These reports can include statistics tables, graphs, images of your sequences, and your own notes. Reports are saved in Geneious Biologics as a record, and can also be exported as PDFs to store in ELNs or other record keeping systems. You can read more about the full functionality here.

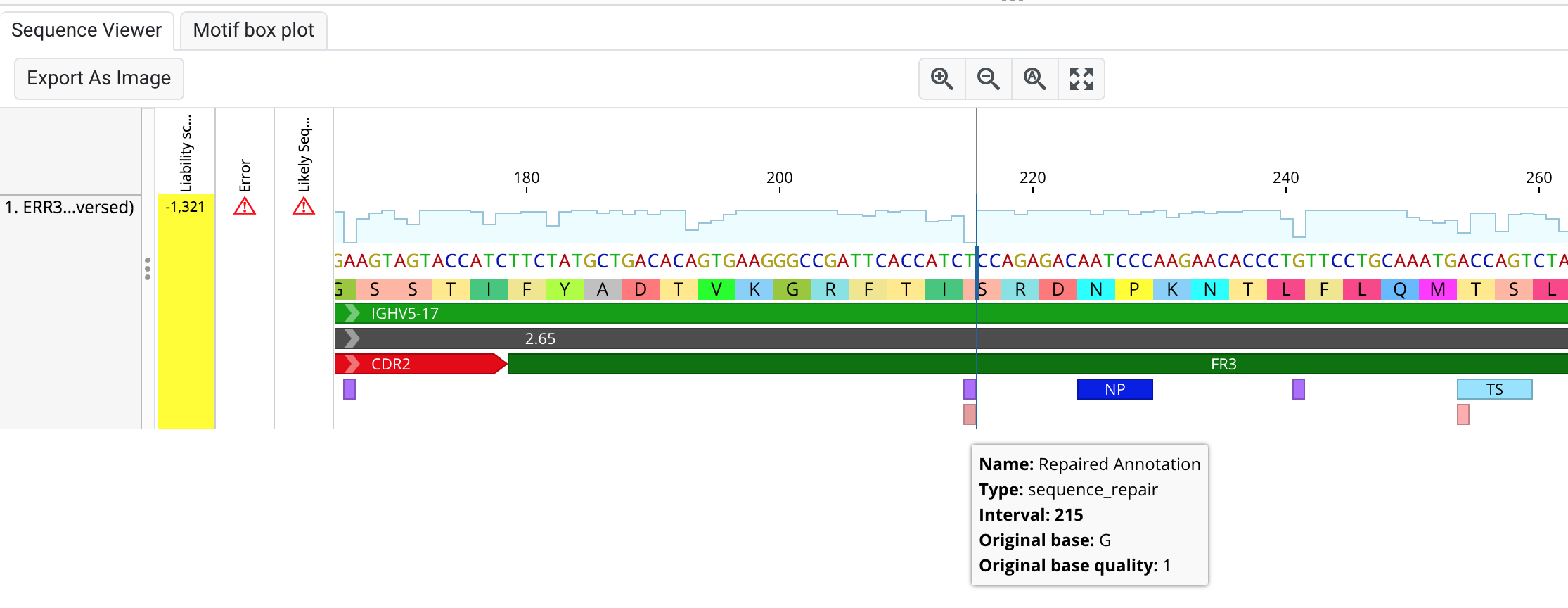
Automated Sequence Repair
In standard Ig-like antibodies, sequence quality can often be low in certain regions, such as at the beginning of FR1 regions or the end of FR4. Sometimes these regions can even be truncated, making extracting a viable candidate sequence difficult. Our latest pipeline "Automated Sequence Repair" aims to solve this problem for you by replacing poor quality or missing regions with bases from their closest germline match. This is just a first alpha version, and we hope to cover more repair scenarios in the future. The full details for the Sequence Repair pipeline can be found here.
Upload Improvements
We are continuing to improve the reliability and convenience of uploading files. In particular, we have enhanced our upload table to show more information about your upload, including specific error messages that should help if anything unexpected happens. We also have a new upload FAQ and troubleshooting guide here.
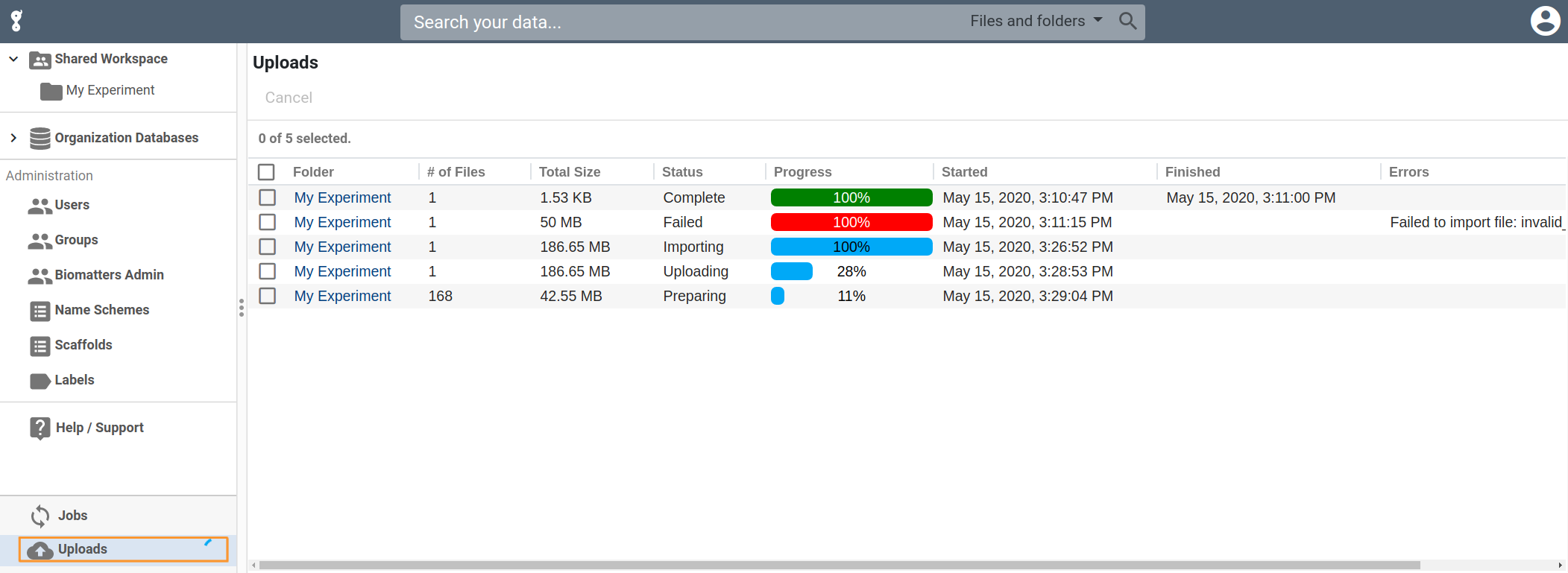
Our latest infrastructure improvements also include some significant speed improvements for upload of individual sequences. For example if you are uploading 96 .ab1 files, your upload and import time should now be greatly improved. Don't worry we haven't forgotten larger datasets either, improvements for upload of NGS-size files are currently in the works.

Our latest infrastructure improvements also include some significant speed improvements for upload of individual sequences. For example if you are uploading 96 .ab1 files, your upload and import time should now be greatly improved. Don't worry we haven't forgotten larger datasets either, improvements for upload of NGS-size files are currently in the works.
Database Types
We have received feedback that creating new reference databases can be confusing, and so we are making some changes to help streamline this process. The first change is to introduce Reference database "types". These correspond to the different ways reference databases can be used, such as the crucial Germline databases for Antibody Annotator. A full description of the different types is available here. From now on you will need to specify a type when creating a new database. Please feel free to ask if you are unsure which type this should be.
Our next big feature coming up is "Master databases", which will offer a way of curating sequence repositories, and then comparing your newly analysed sequences against these repositories. This aims to help answer the question, "Have I seen this sequence before?". It will also help identify closely related sequences.
Amongst other things, we are also making some improvements to alignments, including the ability to align multiple sequence regions together in a flexible way, and the ability to "pick" candidate sequences from alignments and save labels marking your chosen sequences.
Amongst other things, we are also making some improvements to alignments, including the ability to align multiple sequence regions together in a flexible way, and the ability to "pick" candidate sequences from alignments and save labels marking your chosen sequences.
