-
The Reference Database(s) selected can be of antibody germline sequences or of template (variable region) sequences. Reference database(s) are used to help identify the correct FR and CDR regions in the new sequences being analyzed. See Understanding Reference Databases.
-
Your Biologics account will include Human, Mouse, and Alpaca Ig germline databases. If you would like to access to other germlines, please either contact us or see How to make a Custom Reference Database.
- Multiple reference databases can be selected, for example to compare hybridized datasets including Human and Mouse germline genes.
Sequence region of interest is between:
- To define what a "fully annotated" sequence is, you can select the values from the dropdown menu. The default values between FR1 and FR4 means that a sequence is considered to be fully annotated if it consists of all of the regions: FR1, CDR2, FR2, CDR2, FR3, CDR3, and FR4.
Collapse regions at least:
- This option will collapse "identical" sequences up to a percentage threshold of identity. The most frequently occurring sequence from within the group is taken forwards to the results and the count of sequences collapsed will be listed.
- Note that the collapsed sequence includes both the "Sequence region of interest is between" option above as well as the "Retain upstream/downstream of fully annotated region" bp sequence if selected below.
- It is recommended to use an identity percentage low enough to capture sequencing errors but high enough to preserve true variation. 97% is a reasonable default.
Retain upstream and downstream of fully annotated region:
- These options retain up to the specified number of nucleotides upstream/downstream of the Sequence region of interest (explained above) when trimming the ends of contigs. Up to the specified bp will be retained, and sequences will only be collapsed if they have the same length after including the retained bp - in addition to meeting the identity threshold.
Associate significant dominant heavy and light pair
-
This option is recommended for barcoded data or sequencing data from separate sequence lists that represent identical samples. If heavy and light chains are present under the same barcode/sequence list, a Chain Combinations table will be generated. This table will enumerate the possible heavy/light chain pairings found under the same barcode/sequence list.
- Note that this only pairs the 4 most prevalent heavy and light chains that meet the significance threshold (see the filtering section).
Keep unmerged reads
- This option specifies that paired reads which failed to merge should be used in the next step of the pipeline. In use cases where sequence reads are expected to overlap, discarding unmerged reads is recommended in order to improve assembly accuracy.
De novo assembly
- Select this option to perform de novo assembly if the reads constitute fragments of the sequenced region of interest - these will be stitched together to form full sequences.
- This is only recommended if you have performed a barcoded analysis as reads will be assembled into full sequences within the same barcode. Performing this on non-barcoded sequences will result in undesired results, as sequence assembly is performed on the entire dataset.
Analysis Options
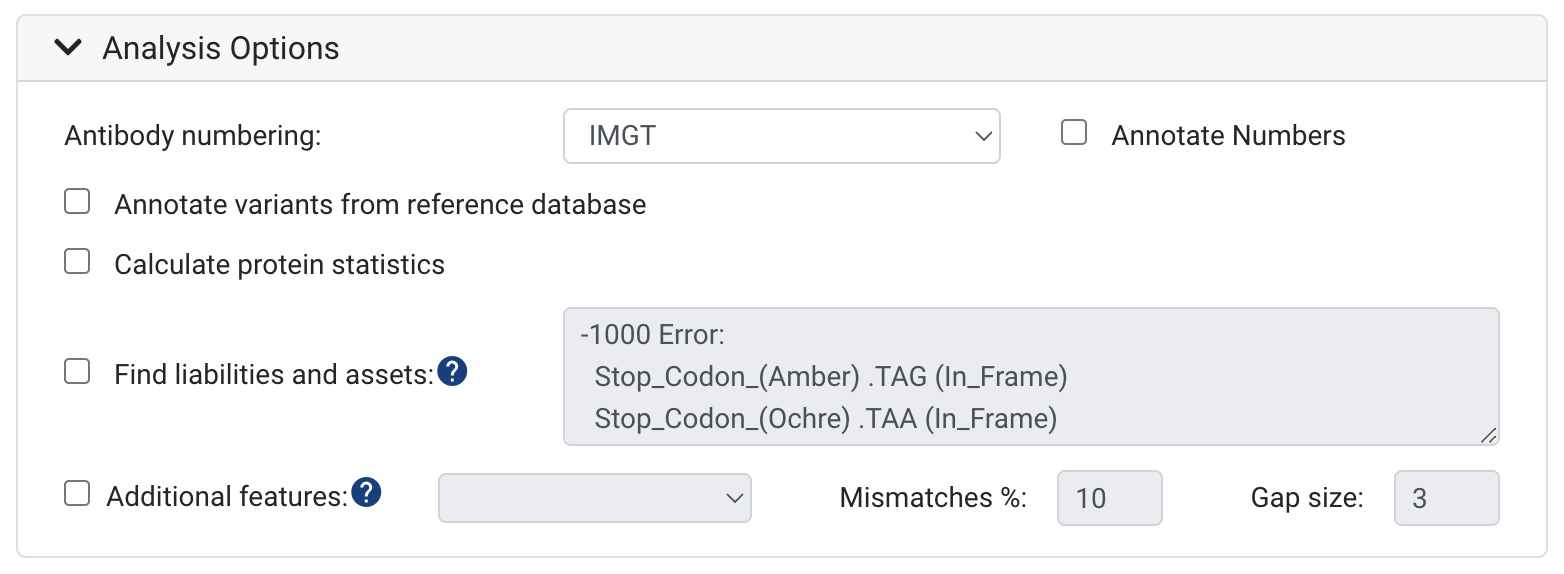
Antibody numbering:
- The default scheme is IMGT CDR definitions and numbering. We support IMGT, Kabat, Chothia, Martin and AHo schemes. To learn more, see Numbering Schemes. You can also turn on and off annotating the numbers on your sequences here.
Annotate variants from reference database
- To annotate and see the differences between your input sequences and reference sequences, select the Annotate germline differences option. With the selection of this option, the nucleotide and amino acid differences will be annotated on your input sequences.
Calculate protein statistics
- This will calculate the Molecular Weight (kDa), the Isoelectric point, the charge at pH 7 and the Extinction Coefficient across the VDJ or VJ region - or both. If a full V(D)J Region can not be found these values will not be calculated.
Find liabilities and assets:
- To search and score amino acid or nucleotide motifs associated with deleterious post-translational modifications or any type of reduced antibody function or desirable motifs, select this option. Biologics has a default set of sequence liability checks, these include: cleavage, deamidation, glycosylation, hydrolysis, isomerization and oxidation. To learn how to specify your own liabilities, see this article: How to customize antibody sequence liabilities and assets
Additional features:
Filtering Options
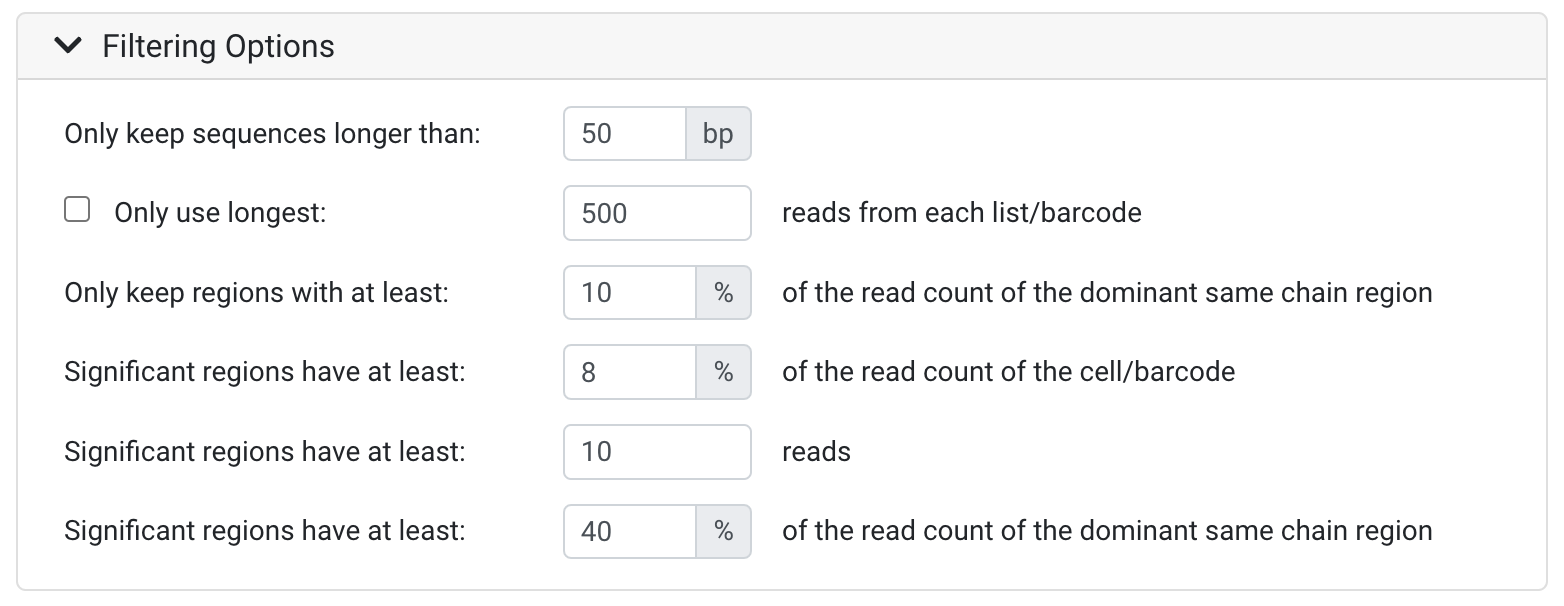
Only keep sequences longer than:
- All sequences that are shorter than the threshold defined will be discarded. This is useful to remove likely low quality sequences. You may wish to set this parameter lower if your sequences have adapters, UMIs and/or barcodes which have been trimmed in the Collapse UMI Duplicates and Separate Barcodes operation.
Only use longest:
- This option lets you specify the number of the reads that will be used from each list or barcode (after sorting by length), with any additional reads discarded. This helps improve performance on large data sets where excessive data significantly slows down analysis. 500 reads is generally sufficient.
- Generally this is not recommended for de novo assembly
Only keep regions with at least:
- This input field lets you discard sequences where the number of reads is equal to or less than the number of reads for the most prevalent chain within the barcode/dataset, specified as a percentage. This setting allows you to permanently discard regions that do not have enough supporting data for further analysis.
Significant regions
Significant region thresholds allow you to filter out infrequent regions to retain statistically significant regions for downstream analysis. Regions deemed insignificant are retained but annotated as not significant.
-
The Significant regions have at least (percentage read count of the cell/barcode) input field lets you flag sequences with low numbers of reads relative to the total reads in the cell, specified as a percentage.
- The Significant regions have at least (reads) input field lets you flag sequences with low numbers of reads as not significant. This is useful for filtering out sequences that were only defined due to reads of very low frequency or due to sequencing errors.
- The Significant regions have at least (percentage read count of the dominant same chain region) input field lets you flag sequences where the number of reads is equal to or less than the number in the dominant same chain region (the one with the most reads), specified as a percentage. This setting allows you to filter out regions that do not have enough supporting data for further analysis.
Note: The chain combinations table will only be produced if at least one heavy and one light chain reaches the significance thresholds above, and can be found in the same barcode/well.
Clustering Options
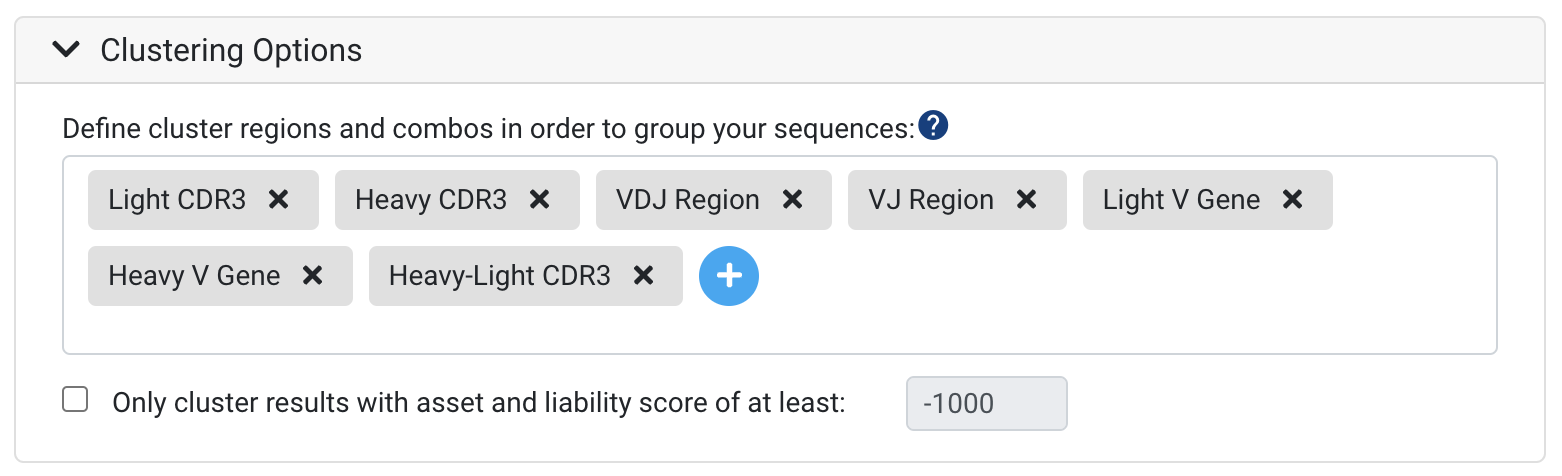
Clustering provides a way to specify clonotype parameters and to group your sequences based on genes or regions of interest. To learn more about clustering and how it can help with interpreting your dataset, see Understanding "Clusters".
Several default clusters will already be listed, and further clusters can be added using the blue "Plus" sign as seen above. Any clusters that are not applicable for a particular analyses, such as Light CDR3 in a Heavy chain data set, will be omitted.
Note: at present, combination clusters across paired Heavy-Light chains (paired under the same barcode) like Heavy-Light CDR3 can only be generated when running the initial annotation. If you are interested in specific clusters that combine regions from the heavy and light chains, please make sure to include these in your annotation run.
It is possible to create custom clusters with up to six regions or genes (FR1, CDR3, Heavy D gene etc.), allow mismatches across a region, and/or cluster based on amino acid similarity. To learn more about configuring advanced clustering options, please refer to Clustering Options.
Cluster Filters
In general, most NGS datasets are relatively large and contain low quality sequences and noise. In order to improve the meaningfulness of clusters in your results, select the following options:
-
Only cluster results with asset and liability score of at least - This option can help to speed up the run-time for large datasets. Sequences will be clustered based on whether they meet the score specified. For example, if you specify a score of -1000, only sequences that have a liability and asset score of -1000 or more will be included in the clusters.
Advanced Options
Document name scheme:
